 Leukemia
Symptoms
Leukemia
Symptoms Leukemia
Symptoms
Leukemia
SymptomsIn a healthy human, red blood cells circulate oxygen throughout the body, while white blood cells protect against infection. When a person has leukemia, the malformed leukemic cells replace and block the production of normal cells, causing this system to fail. The most common symptoms of leukemia results from the collapse of the blood's normal functions. Leukemia patients often experience a variety of indeterminate symptoms, such as weight loss or joint pain, before their diagnosis. The symptoms of leukemia include:
Anemia, caused by a lack of red blood cells. Patients tend to suffer from weakness, fatigue, and malaise, and their skin may look pale from anemia. When exercising, anemic patients may feel faint or experience shortness of breath.
Leukopenia, caused by a lack of normal white blood cells. Patients show increased susceptibility to infection. They may be slow to heal from minor injuries or experience skin or organ infections.
Neutropenia, caused by a lack of mature neutrophils.
Thrombocytopenia or thrombocytosis, caused by a lack of platelets or an abundance of malfunctioning platelets, respectively. Leukemia patients may exhibit increased bruising or bleeding. Signs of this are petechiae, tiny blood spots from capillary hemorraghing, or inexplicable bleeding from seemingly minor injuries.
Enlarged lymph nodes, spleen, or liver, caused by the accumulation of leukemic cells.
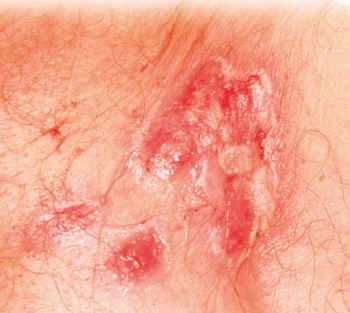
Skin lesions, caused by leukemic cells invading the skin layers.
 Many
cancers begin in a specific organ as a tumor. Once they grow large
enough, they begin “metastasis,” the stage at which cancerous
cells enter the blood and begin circulating throughout a patient's
system, “infecting” new organs. This is the most threatening
cancerous stage for many patients. In leukemia, this dangerous cancer
stage happens immediately, because leukemia originates in the blood
and cycles throughout the body during the entire course of the
disease. This mobility accounts for the variety of specific symptoms
that leukemia causes. If leukemia spreads to the lining of a
patient's brain or spinal cord, he or she may feel “central nervous
system effects, such as headaches, seizures, weakness, blurred
vision, balance difficulties, or vomiting” (Oncology Channel,
1998).
Many
cancers begin in a specific organ as a tumor. Once they grow large
enough, they begin “metastasis,” the stage at which cancerous
cells enter the blood and begin circulating throughout a patient's
system, “infecting” new organs. This is the most threatening
cancerous stage for many patients. In leukemia, this dangerous cancer
stage happens immediately, because leukemia originates in the blood
and cycles throughout the body during the entire course of the
disease. This mobility accounts for the variety of specific symptoms
that leukemia causes. If leukemia spreads to the lining of a
patient's brain or spinal cord, he or she may feel “central nervous
system effects, such as headaches, seizures, weakness, blurred
vision, balance difficulties, or vomiting” (Oncology Channel,
1998).
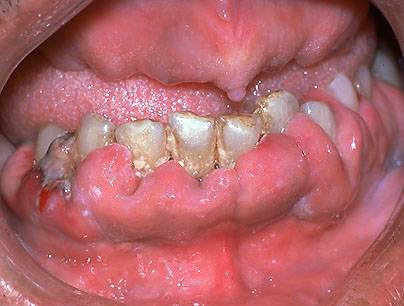
In addition to the common symptoms, some types of leukemia produce distinctive symptoms; for example, if AML spreads to the gums, they may swell or bleed, and if the T-cell variety of ALL spreads to the throat, it may cause coughing or suffocation (Oncology Channel, 1998).
The symptoms of leukemia are severe, and even the chronic forms are likely to substantially reduce the fitness of a leukemia victim. Why, then, is leukemia still present in the population?
Created by Shannon McGlauflin, Jolene Munger, and Rebecca Nelson, 2005.